-
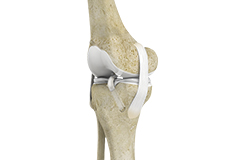
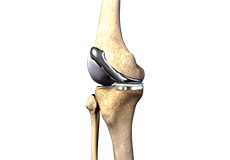
Total Knee Replacement
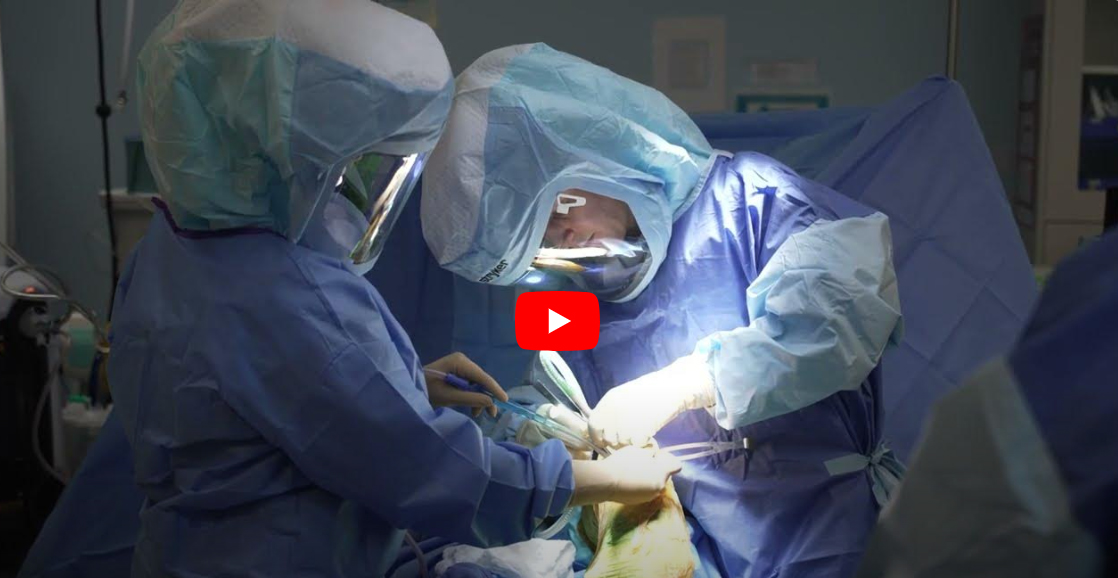
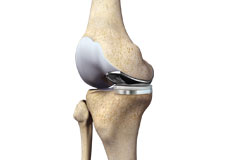
Total knee replacement, also called total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which the worn out or damaged surfaces of the knee joint are removed and replaced with an artificial prosthesis.
-
Unicondylar knee Replacement
Unicompartmental knee replacement or unicondylar knee replacement is a minimally invasive surgery in which only the damaged compartment of the knee is replaced with an implant. It is also called a partial knee replacement.
-
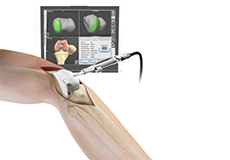
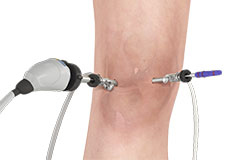
Computer Navigation for Total Knee Replacement
Computer navigation provides your surgeon with real-time 3-D images of your mapped knee and the surgical instruments during surgery. The data for the images is provided by infrared sensors fixed to the bones of the knee and surgical instruments. Their position is tracked by an infrared camera placed above the surgical table, which is connected to a computer.
-
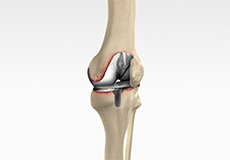
Revision Knee Replacement
Revision knee replacement surgery involves replacing a part or all your previous knee prosthesis with a new prosthesis. Although total knee replacement surgery is successful, sometimes the procedure can fail due to various reasons and may require a second revision surgery.
-
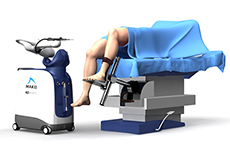
ROSA Robotic Total Knee Replacement
ROSA® Robotic Knee System for total knee replacement is indicated for individuals with early-to-mid-stage osteoarthritis of the knee exhibiting symptoms such as knee pain, knee swelling, and knee locking, that is not amenable to conservative treatment.
-
Minimally Invasive Knee Joint Replacement
Minimally invasive surgery for knee replacement involves the use of smaller incisions which are only 4 to 6 inches in length as compared to the 10-12 inch long incision used in the traditional procedure.
-
Outpatient Unicondylar Knee Replacement
A unicondylar knee replacement, also known as unicompartmental or partial knee replacement, is a procedure to replace a portion of the damaged knee joint with a prosthetic implant to relieve pain and improve function of the knee joint.
-
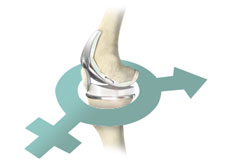
Gender-Specific Knee Replacement
Gender-specific knee replacement, also known as woman’s knee replacement, is a surgical procedure in which gender-specific knee implants specifically designed for a male or female are used for total knee replacement surgery.
-
Complex Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement, also called total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical treatment for painful arthritis of the knee in which the worn-out or damaged surfaces of the knee joint are removed and replaced with an artificial prosthesis.
-
Outpatient Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement is the surgical treatment for knee arthritis, where the damaged knee is removed and replaced with an artificial knee implant. Traditionally performed as an inpatient procedure, total knee replacement surgery is now being conducted on an outpatient basis, allowing you to go home on the same day of the surgery.
-
Partial Medial Knee Replacement
Partial medial knee replacement is a surgery to replace only the medial part of your damaged knee. It is also called unicompartmental knee replacement.
-
What is New in Knee Replacement
If you are considering knee replacement surgery, there are new developments under study which can help enhance the quality of life.
-
Custom Knee Replacement
Custom Knee Replacement is an advanced surgical procedure in which the damaged knee joint is replaced by a customized implant, specifically designed to match the unique size and shape of each patient’s knee.
-
Knee Arthroscopy
Knee arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure performed using an arthroscope, a viewing instrument, to diagnose or treat a knee problem. It is a relatively safe procedure and you will usually be discharged from the hospital on the same day of surgery.
-
ACL Reconstruction
ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) reconstruction is a commonly performed surgical procedure. With recent advances in arthroscopic surgery, it can now be performed with minimal incision and low complication rates.
-
Knee Fracture Surgery
A knee fracture is a broken bone or a crack in or around the joint of the knee. This can involve the tibia (shin bone), the kneecap (patella), or femur (thighbone) where they connect with the knee.
-
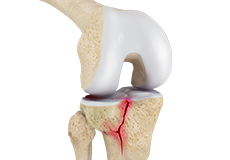
Meniscectomy
Meniscectomy is a surgical procedure indicated in individuals with torn meniscus where the conservative treatments are a failure to relieve the pain and other symptoms.
-
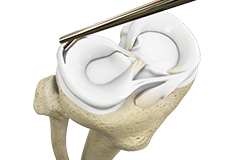
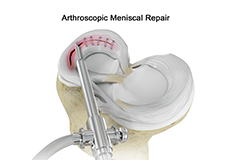
Meniscal Surgery
Meniscal surgery is a surgical procedure employed for the treatment of torn or damaged meniscal tissues in the knee. It is mostly performed as a minimally invasive keyhole procedure.
-
Robotic Assisted Partial Knee Surgery
Robotic-assisted partial knee surgery is an innovative alternative to the conventional surgical procedure to treat degenerative knee diseases such as osteoarthritis.
-
Custom-fitted Total Knee Arthroplasty
Custom-fitted total knee arthroplasty is a newer more advanced technology in total knee replacement surgery that uses an individualized patient-specific knee implant for the replacement of all three components of the knee.
-
Fractures of the Tibia
The lower leg is made up of two long bones called the tibia and fibula that extend between the knee and ankle. The tibia or shinbone is the larger of the two bones.
-
Knee Injury
If the pain and swelling are rapid, then immediate diagnosis and appropriate medical treatment are advised.
-
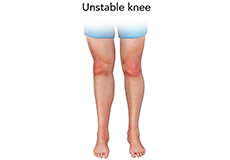
Unstable Knee
The knee joint is one of the largest joints in the body. This highly complex joint has several tissues supporting and stabilizing its movement
-
Knee Sprain
Knee sprain is a common injury that occurs from overstretching of the ligaments that support the knee joint.
-
ACL Tears
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the major ligaments of the knee. It is located in the middle of the knee and runs from the femur (thighbone) to the tibia (shinbone).
-
MCL Tears
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is the ligament located on the inner part of the knee joint. It runs from the femur (thighbone) to the top of the tibia (shinbone) and helps in stabilizing the knee.
-
MCL Sprains
Your MCL may get sprained or injured while twisting, bending or quickly changing direction.
-
Meniscal Injuries
Meniscal tears are one of the most common injuries to the knee joint. It can occur at any age but are more common in athletes involved in contact sports.
-
Meniscal Tears
A meniscal tear is a common knee injury in athletes, especially those involved in contact sports. A sudden bend or twist in your knee causes the meniscus to tear.
-
Knee Arthritis
The joint surface is covered by a smooth articular surface that allows pain-free movement in the joint. Arthritis is a general term covering numerous conditions where the joint surface or cartilage wears out.
-
Knee Pain
Knee pain is a common condition affecting individuals of various age groups. It not only affects movement but also impacts your quality of life.
-
Patella Fracture
The kneecap or patella forms a part of the knee joint. It is present at the front of the knee, protecting the knee and providing attachment to various muscle groups of the thigh and leg.
-
Tibial Shaft Fracture
A tibial shaft fracture is a crack or break in the middle section of the tibia bone due to severe trauma.
-
Knee Fracture
A fracture is a condition in which there is a break in the continuity of the bone. In younger individuals, these fractures are caused by high energy injuries, as from a motor vehicle accident.
-
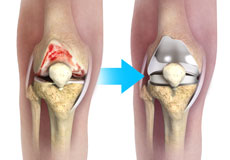
Knee Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis also called degenerative joint disease, is the most common form of arthritis. It occurs most often in older people. This disease affects the tissue covering the ends of bones in a joint (cartilage).
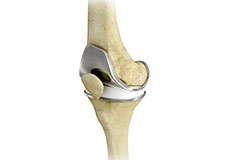
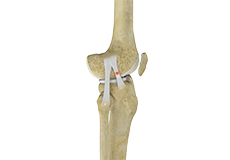
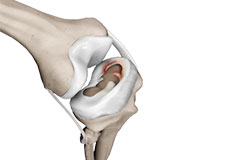
Knee Anatomy
The knee is a complex joint made up of different structures - bones, tendons, ligaments, and muscles. They all work together to maintain the knee’s normal function and provide stability to the knee during movement.
Having a well-functioning healthy knee is essential for our mobility and ability to participate in various activities. Understanding the anatomy of the knee enhances your ability to discuss and choose the right treatment procedure for knee problems with your doctor.
Bones of the Knee
The knee is a hinge joint made up of two bones, the thighbone (femur) and shinbone (tibia). There are two round knobs at the end of the femur called femoral condyles that articulate with the flat surface of the tibia called the tibial plateau. The tibial plateau on the inside of the leg is called the medial tibial plateau and on the outside of the leg, the lateral tibial plateau.
The two femoral condyles form a groove on the front (anterior) side of the knee called the patellofemoral groove. A small bone called the patella sits in this groove and forms the kneecap. It acts as a shield and protects the knee joint from direct trauma.
A fourth bone called the fibula is the other bone of the lower leg. This forms a small joint with the tibia. This joint has very little movement and is not considered a part of the main joint of the knee.
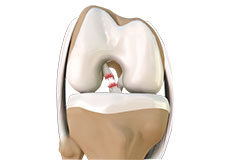
Articular Cartilage and Menisci of the Knee
Movement of the bones causes friction between the articulating surfaces. To reduce this friction, all articulating surfaces involved in the movement are covered with a white, shiny, slippery layer called articular cartilage. The articulating surface of the femoral condyles, tibial plateaus and the back of the patella are covered with this cartilage. The cartilage provides a smooth surface that facilitates easy movement.
To further reduce friction between the articulating surfaces of the bones, the knee joint is lined by a synovial membrane that produces a thick clear fluid called synovial fluid. This fluid lubricates and nourishes the cartilage and bones inside the joint capsule.
Within the knee joint, between the femur and tibia, are two C-shaped cartilaginous structures called menisci. Menisci function to provide stability to the knee by spreading the weight of the upper body across the whole surface of the tibial plateau. The menisci help in load-bearing i.e. it prevents the weight from concentrating onto a small area, which could damage the articular cartilage. The menisci also act as a cushion between the femur and tibia by absorbing the shock produced by activities such as walking, running and jumping.
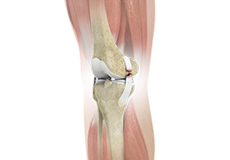
Ligaments of the Knee
Ligaments are tough bands of tissue that connect one bone to another bone. The ligaments of the knee stabilize the knee joint. There are two important groups of ligaments that hold the bones of the knee joint together, collateral and cruciate ligaments.
Collateral ligaments are present on either side of the knee. They prevent the knee from moving too far during side to side motion. The collateral ligament on the inside is called the medial collateral ligament (MCL) and the collateral ligament on the outside is called the lateral collateral ligament (LCL).
Cruciate ligaments, present inside the knee joint, control the back-and-forth motion of the knee. The cruciate ligament in the front of the knee is called anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the cruciate ligament in the back of the knee is called posterior cruciate ligament (PCL).
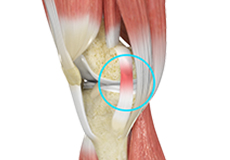
Muscles of the Knee
There are two major muscles in the knee - the quadriceps and the hamstrings, which enable movement of the knee joint. The quadriceps muscles are located in front of the thigh. When the quadriceps muscles contract, the knee straightens. The hamstrings are located at the back of the thigh. When the hamstring muscles contract, the knee bends.
Tendons of the Knee
A tendon is a tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone. The quadriceps muscles of the knee meet just above the patella and attach to it through a tendon called the quadriceps tendon. The patella further attaches to the tibia through a tendon called the patella tendon. The quadriceps muscle, quadriceps tendon, and patellar tendon all work together to straighten the knee. Similarly, the hamstring muscles at the back of the leg are attached to the knee joint with the hamstring tendon.